In this emerging technology, ensuring the reliability, performance, and seamless operation of applications plays an evident role.
This is where observability steps in as a critical component of modern application development and operations, offering a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings of complex software systems.
Observability in modern applications makes your system transparent, which enables you to diagnose and troubleshoot issues before they affect the end user.
Understanding Observability
Observability in modern applications is a measure of how well the internal states of a system can be inferred from knowledge of its external outputs.
In the software context, observability is the knowledge of health and performance in the application that’s gotten through logs, metrics, and traces—the three pillars of observability.
Observability vs. Monitoring
Monitoring involves the collection of data through analysis to identify failure in the system, and in many cases, such data collection protocols are predefined through already known failure modes.
On the other hand, observability is about looking at the unknowns, giving the tools and data necessary to understand and diagnose what was unknown before.
Why Observability Matters
Observability is central to the reliability and performance of any system, and it enables teams to rapidly pinpoint and fix issues, many times before these issues will have an impact on the end users of the system.
It allows teams to understand their system’s behavior in real-time.
2. Understand the system actions in real time.
3. Ability to make informed decisions based on aggregated data.
4. Enhance the system with insights into design and architecture.
Observability Key Components
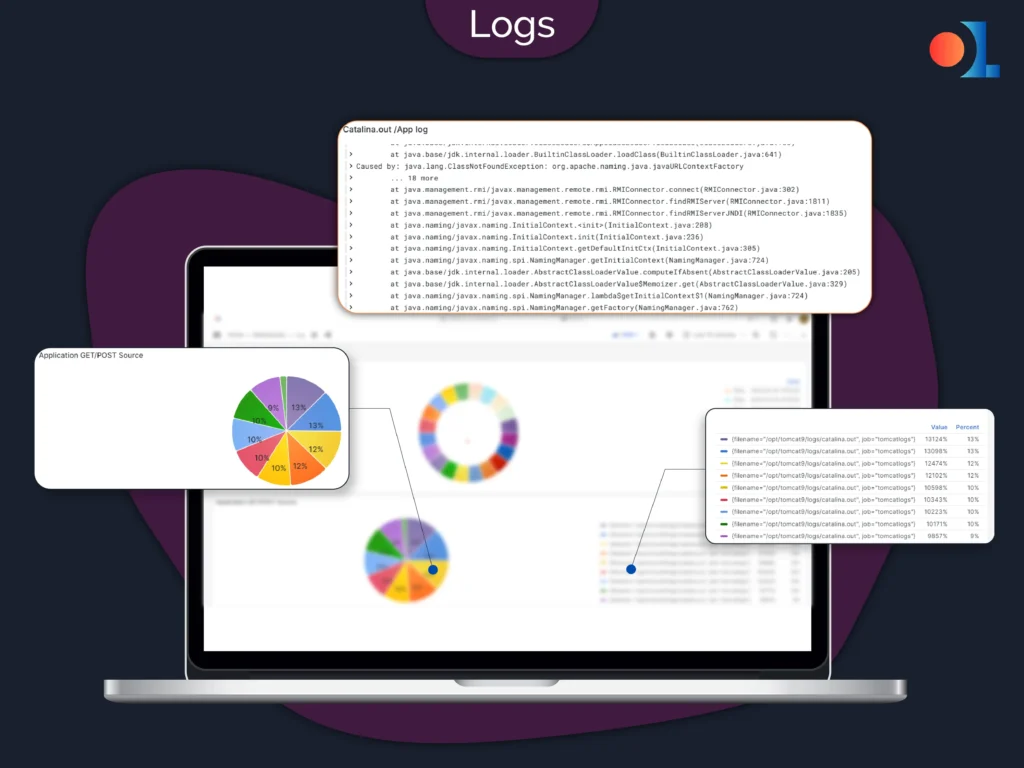
Logs
Logging best practices
Log levels
Metrics
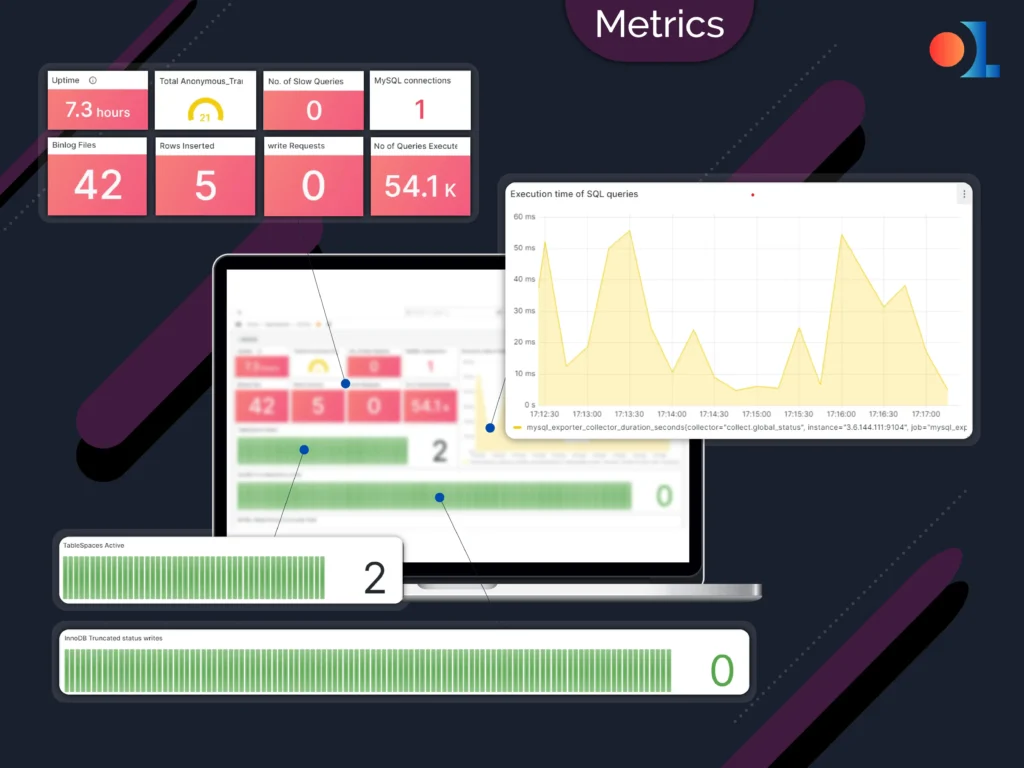
Metrics Collection Types
- Latency: This is the measure of time taken by a system to respond.
- Traffic: The system's demand is measured for your system.
- Errors: Number of failed operations.
- Saturation: Fullness of resources.
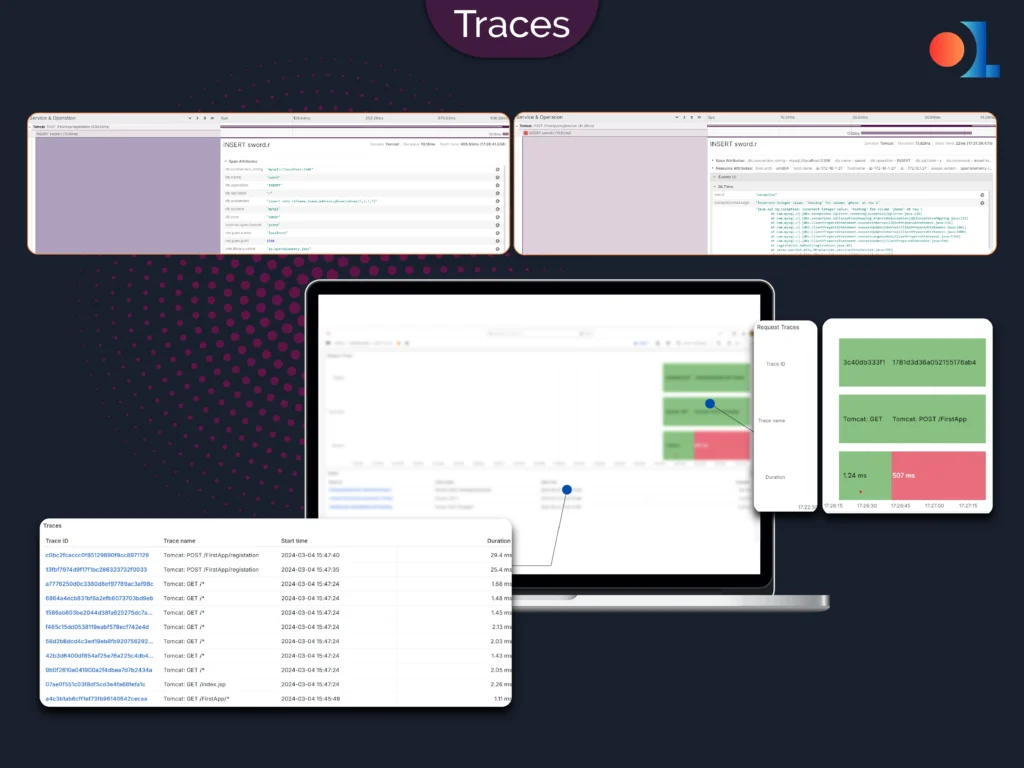
Tracing
Distributed Tracing
Implementation of Observability
How to Scale and Maintain the Observability Setup
2. Regularly keep reviewing and adjusting observability metrics, logs, and traces to ensure they provide insight relevant to your service.
3. Ensure that the observability tools scale up with your application when it experiences increased load and complexity.
Focusing on the key dimensions of logs, metrics, and traces, to develop effective observability practices shall contribute toward better system reliability, performance, and understanding of application.
The observability area for the teams of development and operations’ knowledge and practice is an area that is ever needed and will improve with the technology.